Kia has announced the integration of Extended Range Electric Vehicle (EREV) technology into its product lineup, enhancing the brand’s electrification strategy. EREV technology combines the benefits of a fully electric powertrain with an internal combustion engine that functions as a range extender rather than a direct drivetrain.
How EREV Works
Unlike traditional hybrids, EREVs operate primarily as electric vehicles. The gasoline engine serves only to recharge the battery when needed, offering extended range without relying on external charging infrastructure. This allows users to enjoy the environmental and performance benefits of EVs while minimizing range anxiety.
Key Benefits
- Extended Range: Significantly longer driving distances between charges.
- Better Cold Weather Performance: Improved battery efficiency and energy density.
- EV Driving Feel: Seamless and quiet EV experience with consistent torque delivery.
- Reduced Charging Dependency: Ideal for markets with less-developed charging infrastructure.

Position in Kia’s Strategy
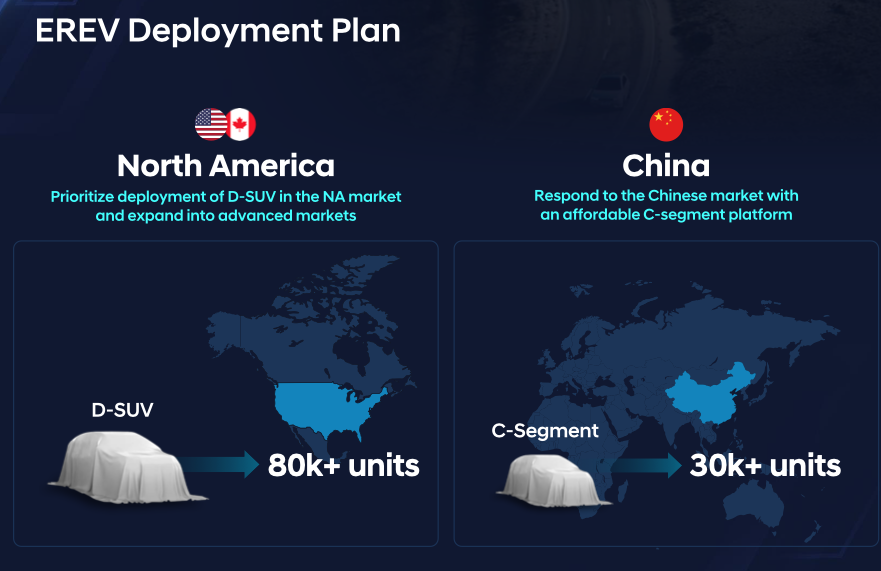
EREV technology will complement Kia’s broader hybrid and EV offerings, especially in regions where EV infrastructure is still developing. It also supports the brand’s transition to Software Defined Vehicles (SDVs) and aligns with its Plan S strategy to offer more flexible and customer-centric electrified mobility solutions.
Hyundai Motor Group’s EREV System
The flagship EREV model for Hyundai will be the Genesis GV70 EREV, a medium-sized sports utility vehicle (SUV) tailored for the North American market. Hyundai will finalize the specifications of this innovative model next month, with a prototype vehicle ready for rigorous testing shortly after.
Production of the GV70 Extended Range will commence in late 2026 at one of Hyundai’s U.S.-based facilities, with a targeted release in 2027. Alongside the GV70, Hyundai plans to extend EREV technology to other popular models, including the Santa Fe, starting with D-segment SUVs that are highly sought after in the North American market.

